| INTERVIEWS WITH HISTORIANS |
|

|
|
|
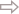
| Following His Teacher as a Model Forever, Research in the History of Science and Technology: An Interview with Wenren Jun |
| HAN Yufen1,2, WENREN Jun3 |
1. Institute for the History of Natural Sciences, CAS, Beijing 100190, China;
2. Huzhou Vocational & Technical College, Huzhou 313000, China;
3. Sunnyvale, California 94087, USA |
|
|
|
Abstract This interview introduces both Professor Wang Jinguang and his student, Mr. Wenren Jun. Topics include their academic inheritance, important events in teaching experience, approaches to research, and teacher-student cooperation. Professor Wang was a trailblazer in the study of the history of physics in ancient China, and was particularly well-known for his research of the history of optics. Professor Wang began to recruit the first graduate students in the history of physics at Hangzhou University in 1978. As one of the two graduate students supervised by Professor Wang from 1978 to 1981, Mr. Wenren has made outstanding achievements in the study of the Kaogong Ji(The Artificers' Record) and the history of Chinese science and technology. His Kaogong Ji Daodu (Guided Reading of the Artificers' Record), published in 1988, won wide acclaim. Routledge published his Ancient Chinese Encyclopedia of Technology, which presents the first English translation of the full text of the Kaogong Ji, in London and New York in 2013.
|
|
Received: 06 December 2018
Published: 18 June 2022
|
|
|
|
Cite this article:
HAN Yufen, WENREN Jun. Following His Teacher as a Model Forever, Research in the History of Science and Technology: An Interview with Wenren Jun. Studies in the History of Natural Sciences, 2019, 38(3): 352-369.
URL:
http://www.shns.ac.cn/ OR http://www.shns.ac.cn/Y2019/V38/I3/352
|
|
|
1 王锦光. 读考工记(中华文化要籍导读丛书)[M]//闻人军. 考工记导读. 成都: 巴蜀书社. 1988. 1~3.
2 戴吾三. 《考工记》中轮之检验新探[J]. 中国科技史料, 2000, 21(2): 147~151.
3 钱伟长. 我国历史上的科学发明[M]. 北京: 中国青年出版社, 1953.
4 竺可桢. 为什么要研究我国古代科学史[N]. 人民日报. 1954-08-27: 3.
5 王锦光, 洪震寰. 我国古代对大气湿度的测定法[C]//科学史集刊. 第9期. 北京: 科学出版社, 1966. 20~23.
6 王锦光. 我国17世纪青年科技家黄履庄[J]. 杭州大学学报, 1960,(1): 1~6.
7 王锦光. 宋代科学家燕肃[J]. 杭州大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 1979,(3): 34~38.
8 徐规, 王锦光. 张荫麟先生的科技史著作述略——纪念张先生逝世四十周年[J]. 杭州大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 1982,(4): 22~25.
9 王锦光, 闻人军. 史学家张荫麟的科技史研究[J]. 中国科技史料, 1983, 4(2): 38~42.
10 王锦光. 浙江集会纪念化学史家王琎教授诞辰一百周年[J]. 中国科技史料, 1988, 9(4): 92.
11 钱临照. 古代中国物理学的成就——Ⅰ 论墨经中关于形学、力学和光学的知识[J]. 物理通报, 1951,(3): 97~102.
12 王锦光, 洪震寰. 中国古代物理学史话[M]. 石家庄: 河北人民出版社, 1981.
13 王锦光, 洪震寰. 中国物理史话[M]. 台北: 明文书局, 1984.
14 王锦光, 洪震寰. 中国古代物理学史略[M]. 石家庄: 河北科学技术出版社, 1990.
15 王锦光, 洪震寰. 中国光学史[M]. 长沙: 湖南教育出版社, 1986.
16 Chemla K. Reviewed Work(s). Zhongguo guangxue shi 中国光学史 by Jinguang WANG 王錦光[J]. Bibliographique de Sinologie, 1987, 5: 313~314.
17 闻人军. 中国物理学史的序幕──评《中国光学史》[J]. 物理, 1986,(8): 519~520.
18 闻人军, 谭峭《化书》四种反射镜考辨[C]//考工司南 中国古代科技名物论集. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2017. 364~367.
19 席文. 科学革命为什么没有在中国发生——它真的没有发生吗?[J]. 闻人军, 余岗, 译. 科学与哲学(研究资料), 1984,(1): 5~43.
20 席文. 评李约瑟《中国科学技术史》第四卷第二分册[J]. 闻人军, 余岗, 译. 王锦光, 校. 科学史译丛, 1985,(1): 1~5.
21 王锦光: 郑复光《费隐与知录》中的光学知识[C]//杜石然. 第三届国际中国科学史讨论会论文集. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990. 8~12.
22 王锦光. 关于"程贞一与中国科技史"一文的订正与补充[J]. 中国科技史料, 1988, 9(4): 92.
23 程贞一. 从公元前五世纪青铜编钟看中国半音阶的生成[C]. 闻人军, 译//曾侯乙编钟研究. 武汉: 湖北人民出版社, 1992. 342~370.
24 郑复光. 镜镜詅痴笺注[M]. 李磊, 笺注. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2014.
25 郑复光. 镜镜詅痴译注[M]. 李磊, 译注. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2015.
26 闻人军. 《考工记》成书年代新考[C]//中华书局编辑部. 文史. 第23辑. 北京: 中华书局, 1984. 31~39.
27 闻人军. 考工记导读图译[M]. 台北: 明文书局, 1990.
28 闻人军. 考工记译注[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 1993.
29 闻人军. 考工记译注[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2008.
30 Wenren J. Ancient Chinese Encyclopedia of Technology: Translation and annotation of the Kaogong ji (the Artificers' Record)[M]. London and New York: Routledge, 2013.
31 林尹. 周礼今注今译 [M]. 台北: 台湾商务印书馆. 1972.
32 汪建平, 闻人军. 中国科学技术史纲[M]. 高雄: 高雄复文图书出版社, 1999.
33 闻人军. "司南之酌"辩证及"北斗说"证误[C]//经学文献研究集刊. 第18辑. 上海: 上海书店出版社, 2017. 20~36.
34 孙机. 再论"司南"[J]. 中国国家博物馆馆刊, 2018,(7): 152~158.
35 闻人军. 再论"司南酌"[C]//中国经学. 第24辑. 桂林: 广西师范大学出版社, 2019: 239~252.
36 闻人军. 原始水浮指南针的发明——"瓢针司南酌"之发现[J]. 自然科学史研究, 2015, 34(4): 450~460.
37 闻人军. 司南酌和指南鱼、针碗浮针传承关系考[M]//考工司南 中国古代科技名物论集. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2017. 262~267.
38 闻人军. "瓢针司南酌"的考古和文献新证[C]//出土文献与古文字研究. 第7辑. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2018. 438~449.
39 徐规, 闻人军. 沈括前半生考略[J]. 中国科技史料, 1989, 10(3): 30~38.
40 汪建平, 闻人军. 中国科学技术史纲(修订版)[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2012.
|
|
Viewed |
|
|
|
Full text
|
|
|
|
|
Abstract
|
|
|
|
|
Cited |
|
|
|
|
| |
Shared |
|
|
|
|
| |
Discussed |
|
|
|
|